
- HOW TO USE TELNET COMMAND IN CISCO PACKET TRACER HOW TO
- HOW TO USE TELNET COMMAND IN CISCO PACKET TRACER SERIAL
- HOW TO USE TELNET COMMAND IN CISCO PACKET TRACER PLUS
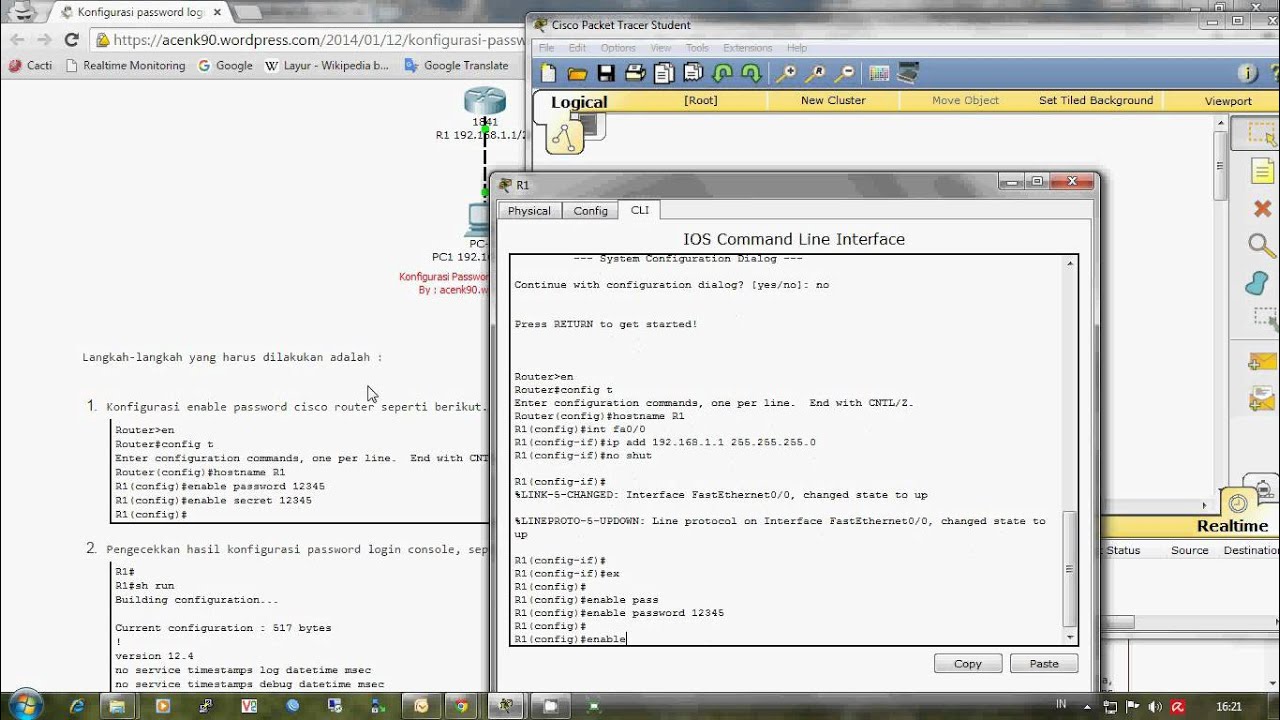
The location command identifies the router’s location to the users. Router(config-line)# location Building-2A Using the line commands, we can define and control access to the console port If you changed any of these defaults on the device, you will have to change the settings on your terminal program to match. The default settings for the port are 9600 baud, 8 databits, no parity, and 1 stop bit. The router responds by starting an EXEC session, which is the process within the router that provides the command-line interface.
HOW TO USE TELNET COMMAND IN CISCO PACKET TRACER SERIAL
To talk to the router just select the correct PC serial interface (the one the console cable is plugged into) and then hit the Enter key a few times. You can use any VT100 terminal-emulation program
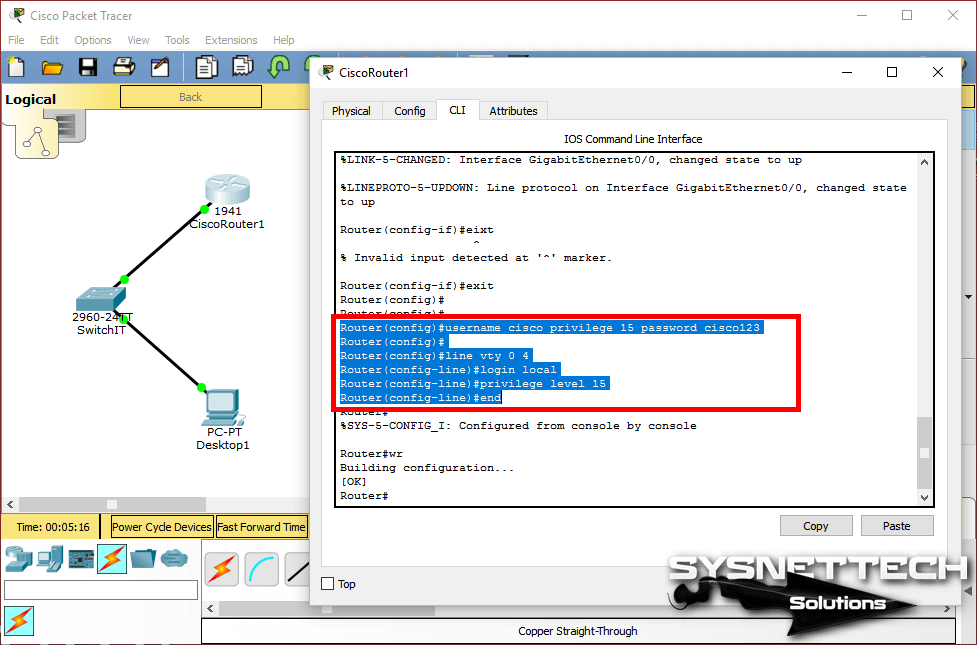
Table 4-1 clarifies absolute and relative line numbering
HOW TO USE TELNET COMMAND IN CISCO PACKET TRACER PLUS
Finally, the VTYs begin at the AUX port’s number plus 1. Next is the AUX port, whose absolute line number is the last TTY number plus 1. If you have eight TTY ports, absolute numbers 1 through 8 will be the TTYs on your router. The TTY ports are next, starting at absolute line number 1 and continuing for the number of TTY lines on the router. The console port is first its absolute line number is zero (0). It would be nice if you could ignore the router’s internal bookkeeping, but a number of commands use absolute line numbers when reporting information about a line’s status.Ībsolute line numbers are calculated by their location on the router, in the order of CTY, TTY, AUX, and then VTY. Internally, the router uses an absolute numbering scheme to keep track of the lines. This numbering scheme is intuitive and convenient. When you’re typing the line command, you give it “relative” line numbers: the first TTY is tty0, the first virtual terminal is vty0, and so on. Instead of typing this command five times, you can configure the entire group with one line command: Router(config)# line tty 5 10 For example, say you want to apply the command exec-timeout to TTY lines 5 through 10. If you want to apply line commands to more than one line, you can specify the starting and ending numbers of a group of lines.
Router(config)# exit Exit the configuration mode Router(config-line)# exit Exit the line configuration mode Router(config-line)# exec-timeout 30 0 Set the timeout to 30 minutes Router(config)#line console 0 Select the console line Router# config terminal Enter configuration mode
HOW TO USE TELNET COMMAND IN CISCO PACKET TRACER HOW TO
The following example shows how to use the line command to configure some properties of the router’s console interface: Router> enable Enter the privileged command mode These line types are discussed individually in this chapter. The possible line types are aux, console, tty, and vty. Here’s the syntax of the line command: line starting-line-number ending-line-number It doesn’t actually do the configuration it is followed by other commands that set up the specific properties you want. The line command specifies which line or group of lines you want to configure by entering the line configuration


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
